The relationship between diabetes and kidney disease. We will explore the complex relationship between these two health conditions, highlighting the causes, symptoms and preventive measures.
Section 1: Understanding Diabetes
To truly understand the connection between diabetes and kidney disease, we must first understand each condition individually. Diabetes is a long-term metabolic disorder that occurs when the body is unable to effectively control blood sugar levels. This affects the body’s ability to produce or use insulin, resulting in increased blood sugar levels, known as hyperglycemia.
Section 2: Role of Kidney
Now, let’s get down to the incredible organs at the center of our discussion today – the kidneys. Kidneys play an important role in maintaining overall health. They filter waste products and extra fluids from the blood, produce important hormones, and control the balance of minerals and electrolytes in our bodies.
Section 3: Diabetic nephropathy – the culprit
Diabetic nephropathy, a specific type of kidney disease, stands as the primary link between diabetes and kidney complications. This condition is caused by uncontrolled high blood sugar levels over a long period of time, which causes damage to the small blood vessels within the kidneys. Over time, this damage impairs the kidney’s ability to effectively filter waste, resulting in a build-up of harmful substances in the body.
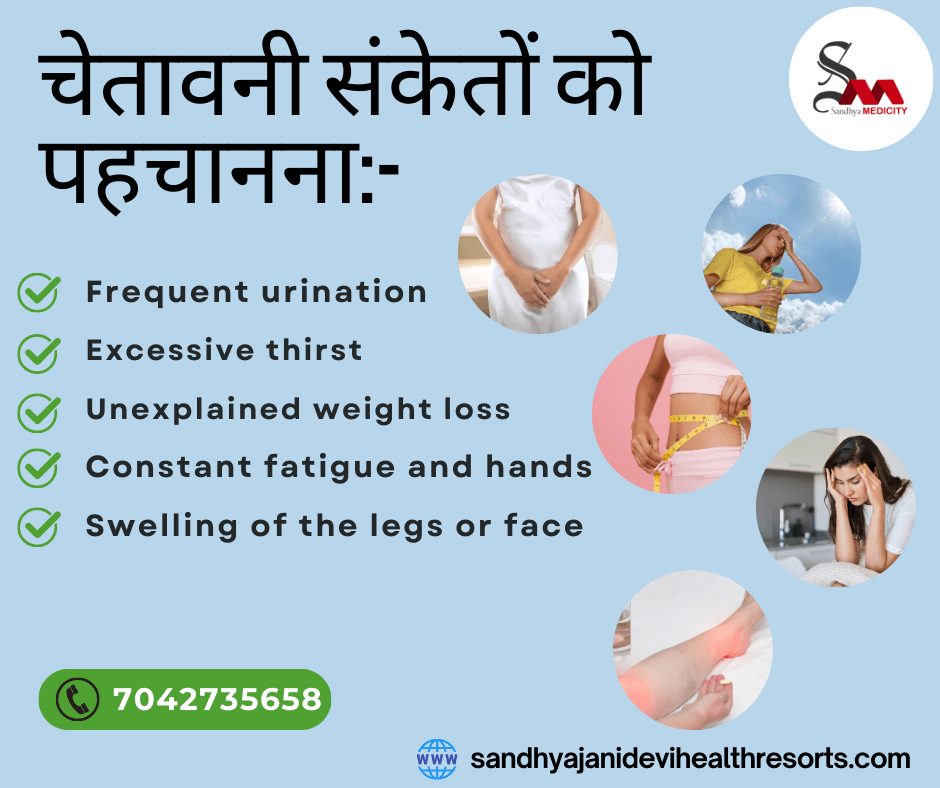
Section 4: Recognizing the Warning Signs
Detection of early warning signs of kidney disease is paramount for timely intervention. Symptoms such as increased urination, excessive thirst, unexplained weight loss, persistent fatigue, and swelling of the hands, feet, or face may indicate kidney failure in people with diabetes. Early medical attention is important to reduce the progression of kidney disease.
Section 5: Is Prevention Possible?
The big question: Can kidney disease be prevented in individuals with diabetes? While genetics and other factors may contribute, maintaining good control of blood sugar levels greatly reduces the risk of developing kidney disease. Regular checkups, blood tests, and consultations with health professionals are important to effectively manage diabetes and prevent further complications.
Section 6: Role of Blood Pressure
High blood pressure, also called hypertension, further increases the risk of kidney disease in people with diabetes. Keeping blood pressure within a healthy range, usually below 130/80 mmHg, is essential to protecting kidney function. Lifestyle modifications, including a healthy diet, regular exercise, and medication prescribed by a healthcare provider, can help achieve optimal blood pressure levels.
Section 7: Treatment Options
If kidney disease is diagnosed in a person with diabetes, various treatment options can be considered. Lifestyle changes, such as adopting a kidney-friendly diet low in sodium and protein, can help slow the progression of the disease. Medications including ACE inhibitors and angiotensin receptor blockers are commonly prescribed to manage high blood pressure and protect kidney function.
Section 8: Advanced Stages – Dialysis and Transplantation
In advanced stages of kidney disease, when kidney function is significantly reduced, dialysis or transplant may be necessary. Dialysis acts as an external filtration system, removing waste products from the blood, while transplantation surgically replaces the damaged kidney with a healthy kidney. These measures can improve quality of life, but prevention and early intervention are always preferred.
Section 9: Lifestyle Modification and Self-Care
In addition to medical interventions, it is important for people with diabetes to adopt a healthy and active lifestyle to prevent kidney complications. Regular physical activity, maintaining a balanced diet, avoiding smoking, limiting alcohol intake, and controlling stress levels can all contribute to the overall health of your kidneys and your entire body.
conclusion:-
As we wrap up today’s video, we want to emphasize the importance of understanding the connection between diabetes and kidney disease. By maintaining good blood sugar control, controlling blood pressure, and adopting a healthy lifestyle, individuals with diabetes can significantly reduce their risk of kidney complications. Remember, early detection, timely treatment and taking active care of your kidneys are important elements of your overall well-being.